The SPRINT-Lab researchers have developed the RADAR-HF Methodology ('Recon Analysis for Detecting the Actual situation and the improvement Requests for Hospital Facilities') to provide essential information for the planning of modernization interventions through a survey of the chosen indicators, allowing to have an overview of the situation of the hospital structure with respect to pre-established objectives.

The RADAR-HF Methodology is based on the following guiding criteria:
- development of a methodology and cost-effective assessment tools, which provide essential information on the situation of the building stock for the planning phase of the interventions;
- development of a tool for monitoring hospital structures, and not a tool for a one-off census, which can be used independently by technicians;
- evaluation of the physical environment of the hospital structures only (management measures or medical activities are not considered);
- hierarchy of relevant indicators, which gives greater importance to safety and functionality;
- performance zoning, i.e. the characterization of spaces with reference to homogeneous functional areas;
- integrated functional analysis, which considers the hospital as a complex system of interrelated activities, activities and support systems, service infrastructures;
- identification of the building's vocation, or its best occupancy, also in relation to safety and functionality in an emergency.
The methodology allows the creation of a "dashboard" in which the outcomes of the assessments of the buildings analysed are reported. The dashboard allows decision-makers to have an overview of the main indicators deemed relevant for the technical investment planning choices of the region's healthcare building stock. The indicators highlight the greater or lesser "intrinsic vocation" of the individual properties to the different potential health conditions of use.
For instance, the COVID-19 pandemic underlines the importance of knowing the physical environment of hospital facilities, to adapt it as quickly as possible in case of impending situations. Decision-makers and technicians can use RADAR-HF as support to face the problem of increase intensive care units.
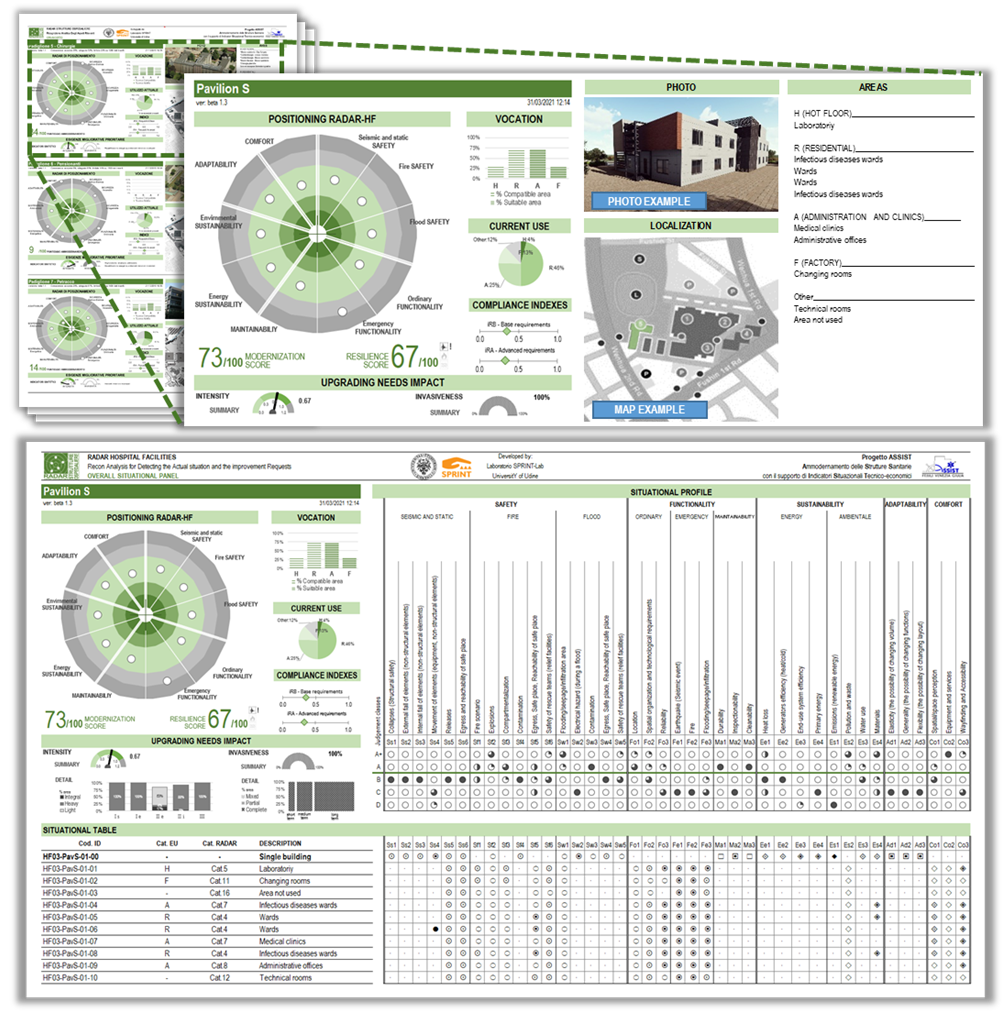
Dashboard and Situational panel
The outcomes of the RADAR-HF Methodology are similar with those used in the methodologies for assessing health services. This makes possible to present the results of technical assessments with a language already used in the medical world. Furthermore, since RADAR-HF is a methodology for evaluating the physical environment only, it will be possible to integrate the RADAR-HF methodology, with the management / medical evaluation tools already in use.
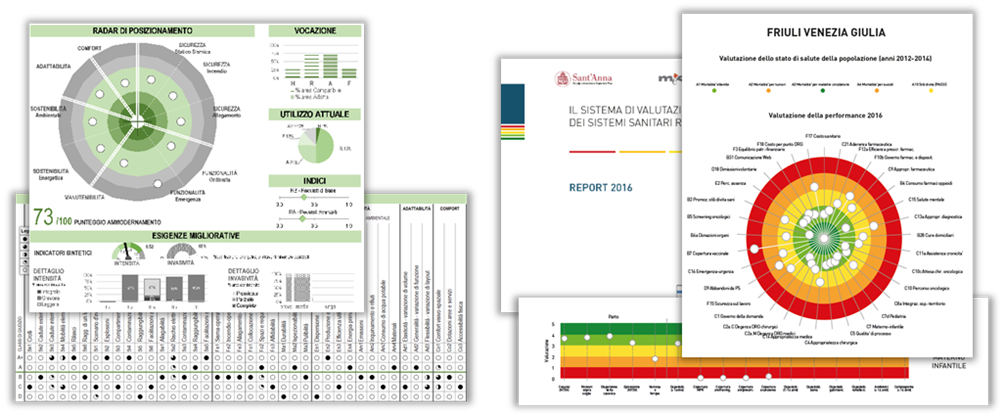
Methodology development
To identify the actions for rationally dealing with the improvement of a situation of a specific entity, a preliminary assessment is required. This assessment should be finalized: a) to characterize the actual situation with respect to all the aspects considered as meaningful and characterizing, b) to identify the gaps between the current and a desired final situation and c) to suggest the interventions necessary to reach the desired target situation. To address these needs, the SPRINT-lab researchers have developed a multi-parameter assessment method, named RADAR (Recon Analysis for Detecting the Actual situation and the improvement Requests).
RADAR method conceptualizes the problem considering an n-dimensional space of situations, where every dimension is related to one main aspect. In this space, each situation can be localized by the n-coordinates; each coordinate represents the position along a dimension. Each dimension has two extremes related to the best and the worst possible situations. The actual position (initial position) can be compared with a desired situation (target position) and the improvement can be conceived as a shift towards a better position.
In order to develop the RADAR-HF methodology, the authors customized the multi-parameter RADAR method carrying out an intersectoral collaborative process with experts and sectoral specialists. This process aims to elicit expert reasoning by using the charrette technique. The customization has concerned objectives of the assessment, main aspects, algorithms, metrics, and outcomes representation.
RADAR-HF considers different main aspects as safety, functionality, sustainability, adaptability, and comfort. The algorithms evaluate the aspects with reference to specific established goals and they are based on a hierarchy of main indicators which assign greater importance to safety and functionality. In addition, the algorithms take into account the relationships between the hospital facilities parts, considering them as complex systems. Graphical indicators and overview-tools represent outcomes. These have been specifically designed to outline the status-condition of one or a set of existing healthcare facilities, the upgrading needs impact, and the best occupancy of the facilities. RADAR-HF has been structured even to be a monitoring tool optimizing and minimizing the input data.
The RADAR-HF methodology was applied in the ASSIST research project (in Italian, ASSIST is the acronym of ‘Ammodernamento delle Strutture Sanitarie con il supporto di Indicatori Situazionali Tecnico-economici’). The ASSIST research project aimed to assess the physical environment of existing hospital facilities of the Friuli Venezia Giulia region (North-East of Italy). The goal of the ASSIST project was to provide the local decision-makers with a strategic vision for defining a modernization plan. An internal group of technicians of the regional healthcare system have used the RADAR-HF methodology for the situational assessment of the existing hospital facilities. The technicians have applied the methodology on one hospital facility after a short period of training and capacity building with the support and review of the authors. Then technicians have collected the data and have produced the outcomes using the RADAR-HF SW-tool for most hospital facilities of the region. The application of RADAR-HF has allowed an overview of the situation of the physical environment of the existing hospital facilities of the Friuli Venezia Giulia region (North-East of Italy).
In summary, the RADAR-HF Methodology allows you to:
- Compare buildings from various points of view (dashboard).
- Explore intervention strategies for modernization.
- Compare functional strategies.
- Evaluate the building's vocation (best occupancy).
- Monitor the state of buildings.



